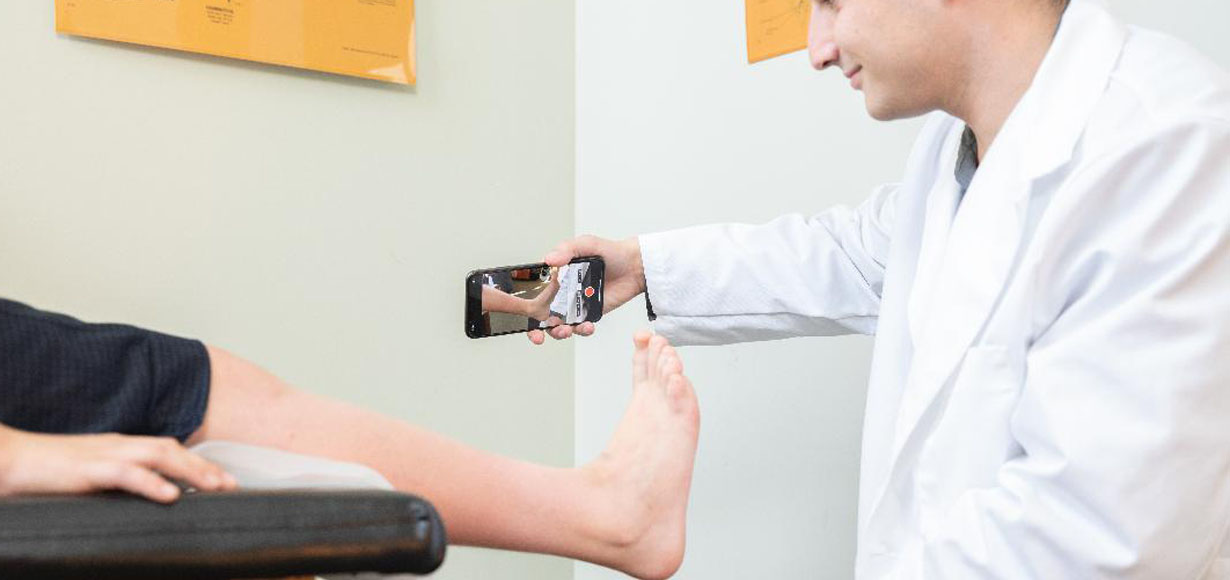
“Digital transformation” is something many people are talking about in many walks of life, including prosthetic and orthotic (P&O) practice and services. For P&O, “Digital transformation” can mean any change to practice due to the introduction of a digital technology that was not used before. The simplest example might be a measurement tool to support a traditional manufacturing method, and the other extreme might be highly disruptive technologies that automate assessment of patients and production of P&O devices, connecting centres across different parts of the same countries or across countries.
We have been asked to develop plans that might help the P&O sector adopt more digital technologies but first we need to understand what is currently being used, and where. This survey aims to capture the current global use of digital technologies by different members of the P&O community and map these by location around the world.
Our team brings together ISPO with members of industry and academics and is not related to any commercial developments. The results of this survey will be published in Prosthetics & Orthotics International Journal
The general scope of this survey comprises:
- External devices for upper limb, lower limb, thoracic, lumbar, cervical, cranial excluding dental, facial and cosmesis for any body part.
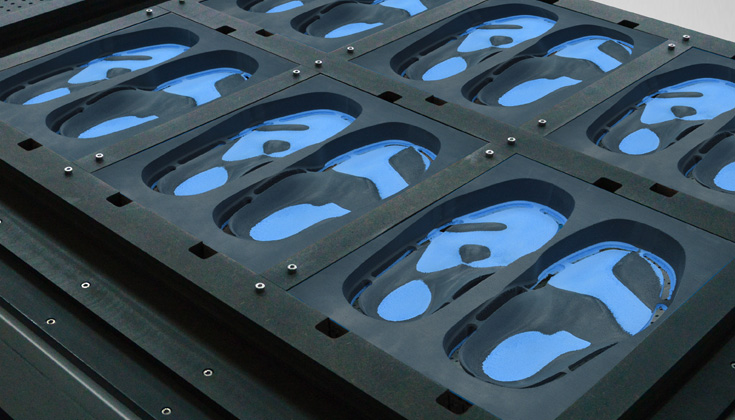
- The complete/partial digital fabrication workflow for all P&O components, ie. all combinations of scanning, virtual rectification, carving, printing (+ any traditional methods if used in unison with digital methods)
- Other digitally fabricated components, ie. components or whole devices usually prefabricated
- Repair/augmentation/replication processes using digital methods
- Clinics across a full range of low to high resource settings.
By filling in this survey you give consent to the participation in this research project. Please see the ethics information sheet found at this link: Ethics Information Sheet
This is a collaborative project including the International Society of Prosthetics and Orthotics, University College London, World Health Organisation, the University of Salford, Jonkoping University, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, University of Southhampton, and the University of Ottawa
Please go to this link to fill in the survey: https://salford.onlinesurveys.ac.uk/global-survey-on-digital-fabrication-of-prosthetics-and-or
Update on data collected so far across 94 respondents
Passive map of respondent territories (an interactive map is in development) with pie charts of breakdown of whether respondents are actively using digital techniques:
(no. on heatmap = no. of clinics using that process currently)